Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? This question is crucial as California faces increasingly devastating wildfire seasons. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting wind patterns—all exacerbated by climate change—are creating a perfect storm for larger, more frequent, and more intense wildfires. We’ll explore the historical trends, examine the impact on vegetation and fuel loads, analyze the role of wind, delve into specific case studies, and discuss how we’re adapting wildfire management strategies in this new reality.
California Wildfires and Climate Change
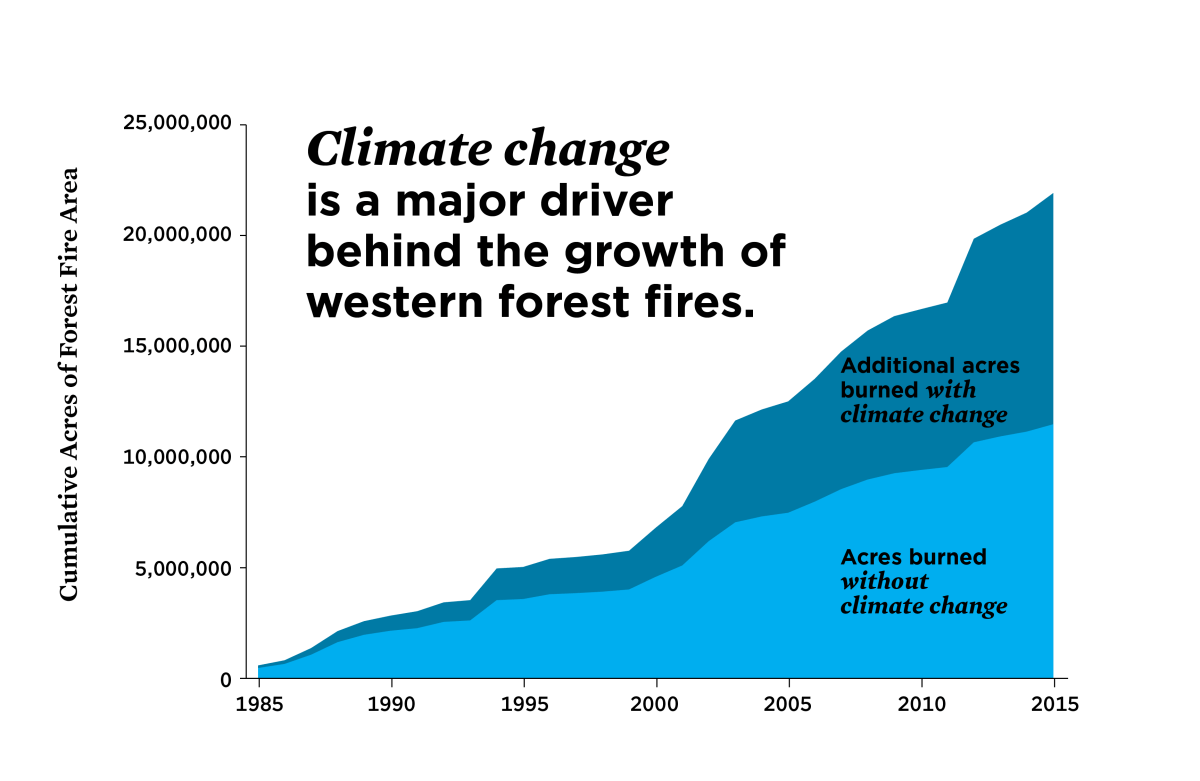
California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and destructive in recent decades. This intensification is significantly linked to climate change, which is altering weather patterns, vegetation, and the overall fire environment. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective wildfire management strategies.
The Impact of Climate Change on California’s Wildfire Season
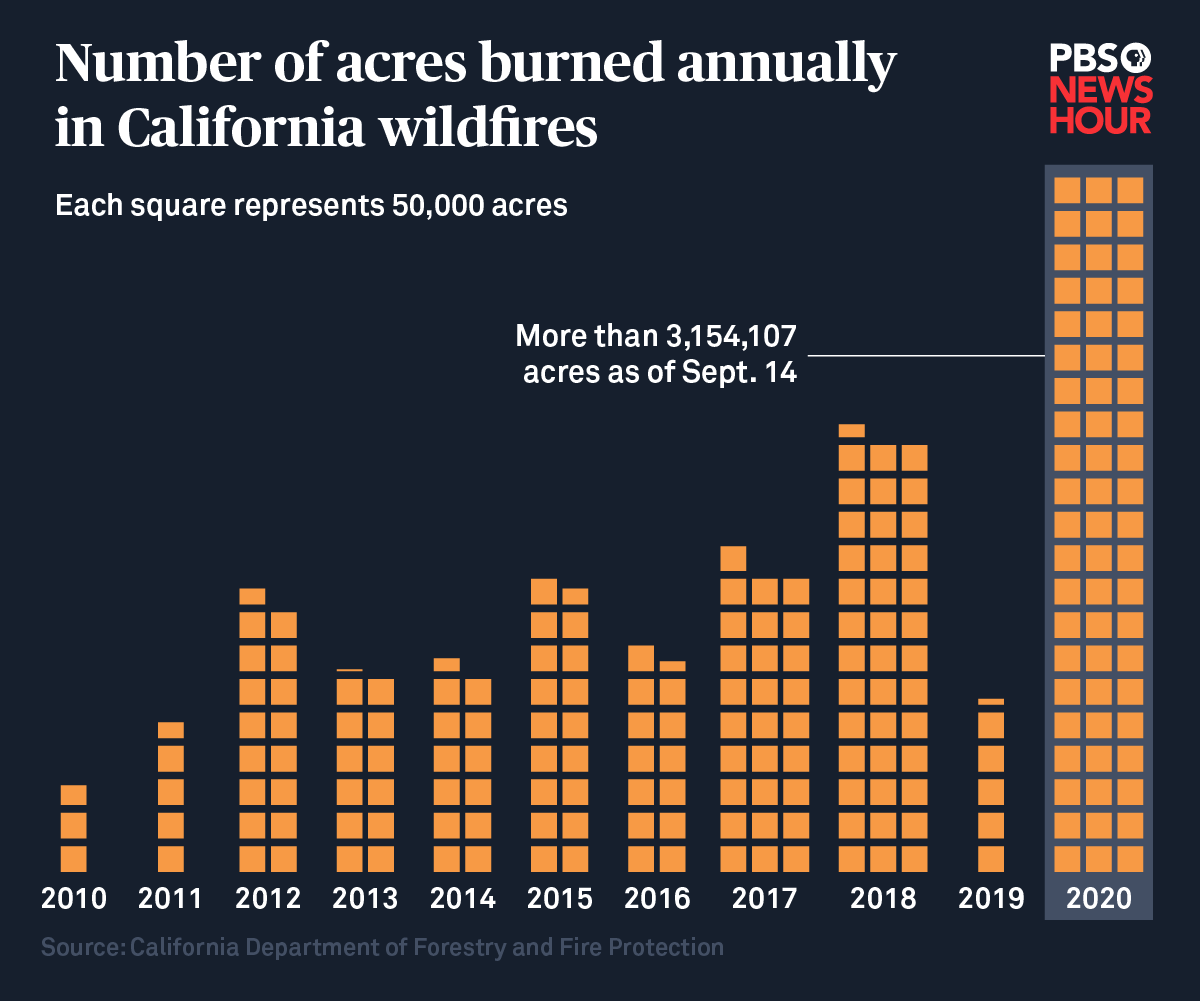
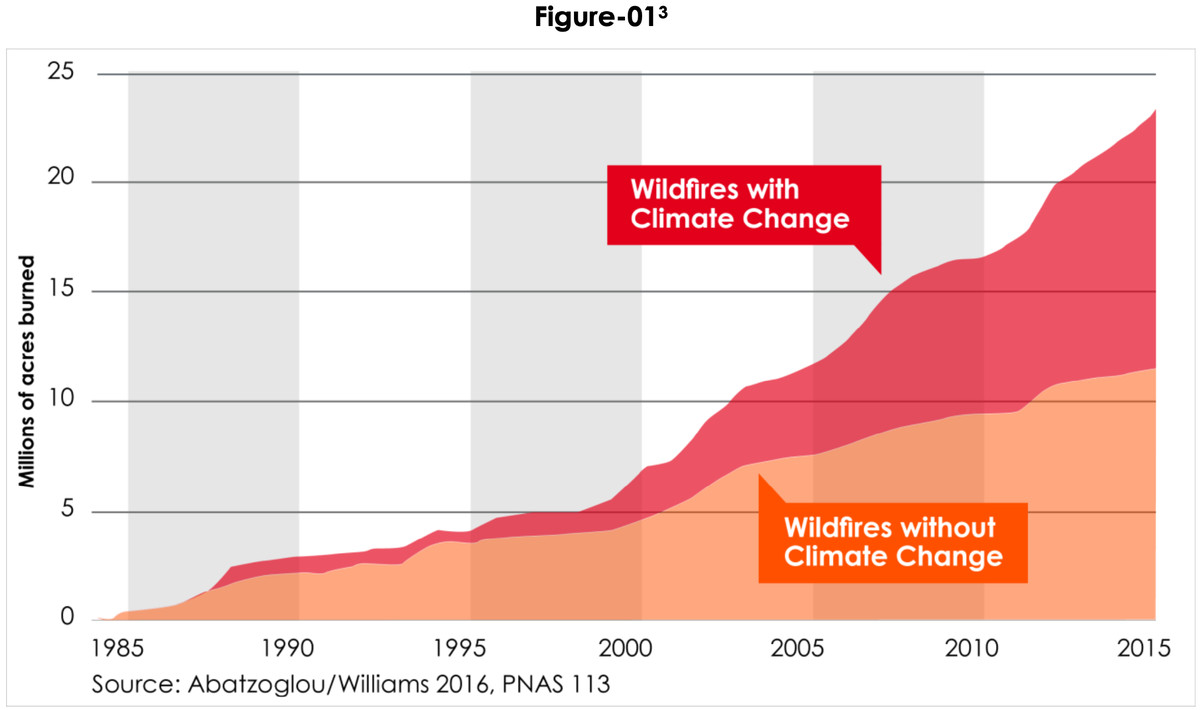
Historical data reveals a clear trend: California wildfires are becoming more frequent, intense, and widespread. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns, all exacerbated by climate change, are the primary drivers of this alarming increase.
Rising temperatures directly increase the flammability of vegetation. Drier conditions, a hallmark of climate change-induced drought, create abundant fuel for fires to spread rapidly. Changes in precipitation patterns, such as earlier snowmelt and more intense rainfall followed by prolonged dry periods, contribute to the timing and severity of fire seasons.
| Decade | Number of Fires | Acres Burned (millions) | Average Fire Size (acres) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1970s | 5,000 (approx.) | 0.5 (approx.) | 100 (approx.) |
| 1980s | 6,000 (approx.) | 0.7 (approx.) | 115 (approx.) |
| 1990s | 7,000 (approx.) | 1.0 (approx.) | 140 (approx.) |
| 2000s | 8,000 (approx.) | 1.5 (approx.) | 185 (approx.) |
| 2010s | 9,000 (approx.) | 2.5 (approx.) | 275 (approx.) |
| 2020s | 10,000+ (approx.) | 3.0+ (approx.) | 300+ (approx.) |
Note: These are approximate figures and vary depending on the data source. Accurate, consistent data collection across decades presents challenges.
Vegetation and Fuel Load in a Changing Climate, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires

Climate change significantly impacts vegetation, making it more susceptible to fire. Increased temperatures and drought stress lead to denser, drier vegetation, creating a higher fuel load. Invasive species, often thriving in altered climate conditions, can further exacerbate the problem by altering plant communities and increasing flammability.
For example, the expansion of drought-tolerant shrubs and grasses in areas previously dominated by more fire-resistant trees increases the overall fuel load and creates continuous fuel beds. This makes fires spread more rapidly and intensely.
Infographic Description: A three-panel infographic would visually represent the relationship. Panel 1 shows a healthy forest with diverse vegetation and moderate rainfall. Panel 2 depicts a forest stressed by drought, with increased density of dry brush and fewer trees, representing increased fuel load. Panel 3 illustrates a raging wildfire consuming the dry vegetation, highlighting the connection between climate change, altered vegetation, and wildfire risk.
Arrows connect the panels to show the causal relationships.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drier conditions and hotter temperatures. It’s a huge issue, and while completely unrelated, it’s interesting to note that completely different negotiations are happening elsewhere; for example, check out this news about a faculty strike being averted: Faculty strike averted at Ontario colleges as both sides agree to.
Returning to California, the increasing intensity of these fires highlights the urgent need for climate action to prevent future devastation.
Wind Patterns and Fire Spread
Climate change is influencing wind patterns in California, increasing the intensity and frequency of strong winds like the Santa Ana winds. These winds, known for their ability to rapidly spread wildfires, are becoming more frequent and intense, contributing to larger and more destructive fires. The altered atmospheric pressure gradients associated with climate change are thought to be a factor in this increased intensity and frequency.
The increased wind speeds significantly impact fire behavior, increasing the rate of fire spread and making firefighting efforts more challenging. The combination of high winds, dry vegetation, and elevated temperatures creates a perfect storm for catastrophic wildfires.
The Role of Climate Change in Specific California Wildfires
The 2020 August Complex fire, one of the largest wildfires in California history, serves as a compelling case study. The prolonged drought conditions, exacerbated by climate change, created an exceptionally dry fuel bed. High temperatures and strong winds further fueled the fire’s rapid spread, resulting in widespread destruction and significant air quality issues across a vast area. The economic losses, including property damage, firefighting costs, and economic disruption, were substantial and directly linked to the climate change-induced conditions.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes you need a little distraction, like checking out this cool exhibit – New Exhibit Celebrates Elvis’ 90th Birthday – before diving back into learning more about how climate change is altering fire seasons and increasing the risk of devastating blazes.
Understanding the connection between climate and wildfires is key to preparing for the future.
Climate Change and Wildfire Management Strategies
Wildfire management agencies face unprecedented challenges in a changing climate. Traditional methods of fire suppression are often insufficient to control the increasingly intense and widespread fires. Adaptations are crucial, including improved early warning systems, more proactive fuel management strategies, and the development of more resilient communities.
- Implementing prescribed burns to reduce fuel loads in a controlled manner.
- Developing more sophisticated fire modeling and prediction tools.
- Investing in improved firefighting technology and resources.
- Promoting community-based wildfire preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Implementing landscape-scale restoration projects to enhance forest resilience.
Ultimate Conclusion
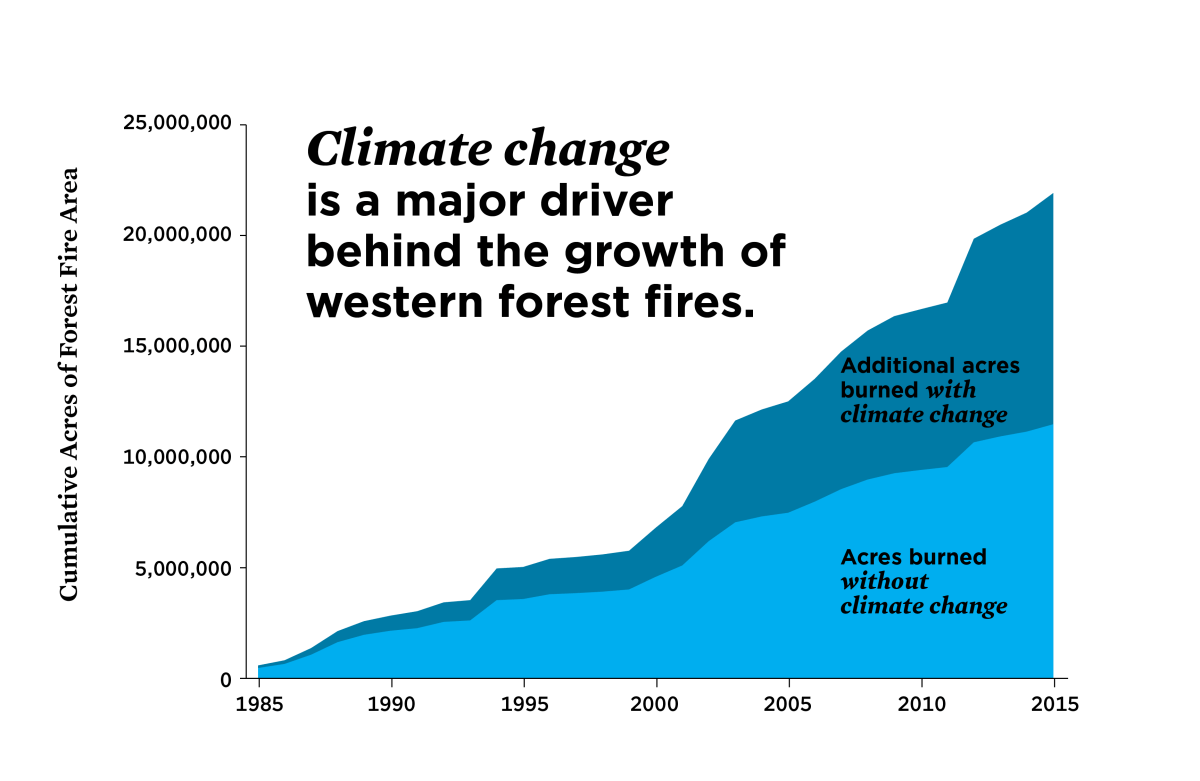
The link between climate change and California’s wildfires is undeniable. While the immediate causes of any given fire are complex, the underlying trend of increasing intensity and frequency is directly tied to a warming planet. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies. From adapting firefighting techniques to implementing long-term land management practices, the challenge lies in confronting the reality of a changing climate and building resilience in the face of increasingly fierce wildfire seasons.
The future of California’s forests, and indeed the safety of its communities, depends on our ability to address this critical issue.
FAQ: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
What specific policies are being implemented to address climate change’s impact on wildfires?
Policies range from forest management practices (like controlled burns and fuel reduction) to stricter building codes in fire-prone areas and investments in early warning systems and improved firefighting technology.
How can individuals contribute to wildfire prevention efforts?
Individuals can help by creating defensible space around their homes, staying informed about fire danger levels, and supporting organizations working on wildfire prevention and mitigation.
What are the long-term economic consequences of these increasingly severe wildfires?
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a massive challenge, and while we grapple with the environmental devastation, it’s interesting to see how other areas are facing change, like the architectural work detailed in this article about Allies & Morrison picked for ‘groundbreaking’ transformation of a project.
Ultimately, though, tackling climate change is crucial to mitigating the increasing severity of these California fires.
Long-term economic impacts include billions of dollars in property damage, lost tourism revenue, increased insurance premiums, and the cost of long-term recovery and rebuilding efforts.